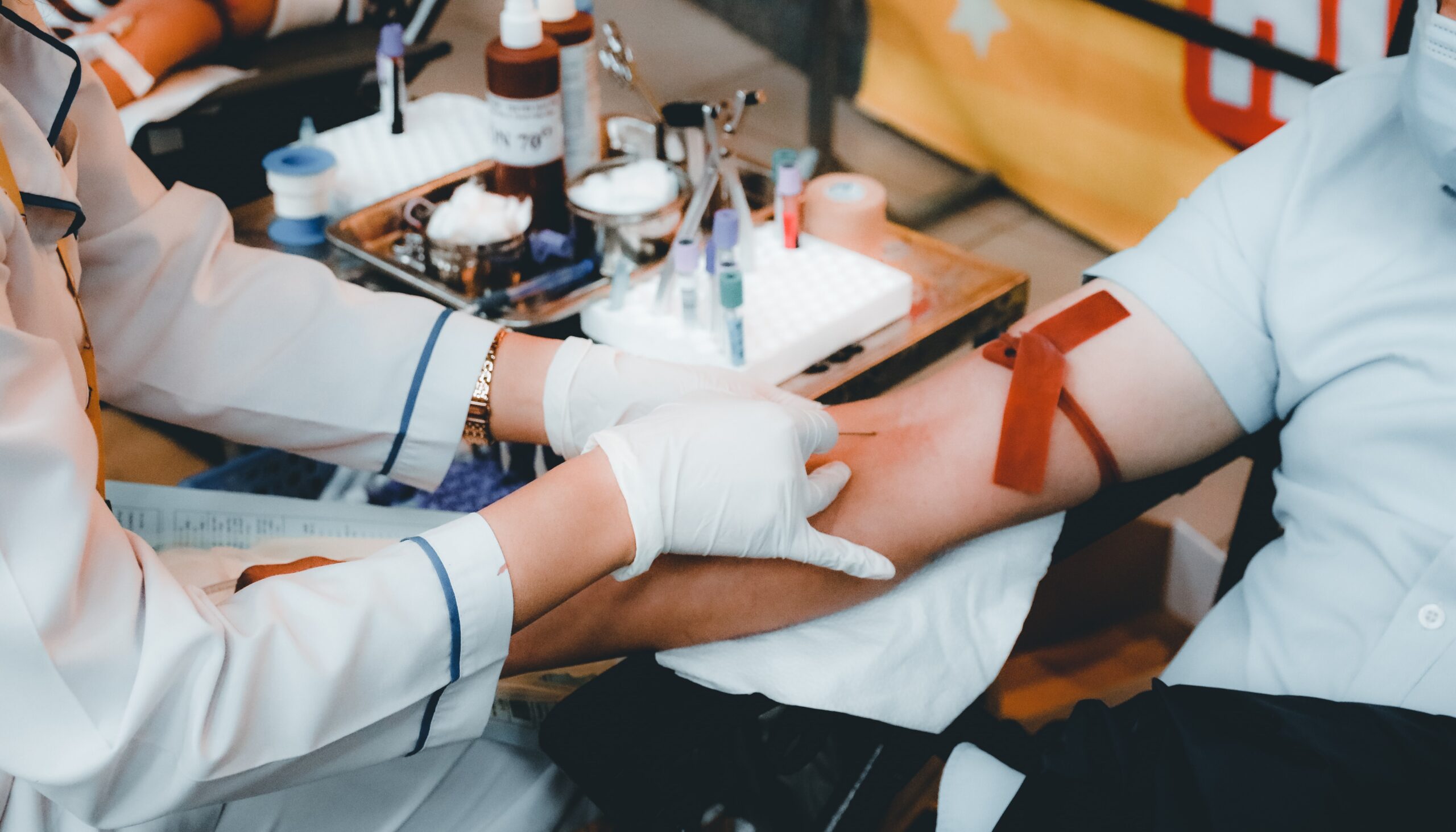
Blood test which tells us about the general health pf the patient. Withdraw blood sample from vein. WBC, RBC, & PLATELETS are included.
WHITE BLOOD CELL AND ITS TYPES
White blood cell is also known as LEUKOCYTES, main role is to fight against the infections. WBCs is of 5 types: Basophils, Eosinophils, Monocytes, Neutrophils, Lymphocytes. BASOPHILS: involved in allergic response. EOSINOPHILLS: kill parasites, cancer cell, also involved in allergic response. MONOCYTES: clean up the damaged cells. NEUTROPHILLS: kill bacteria, fungi, and foreign debris. LYMPHOCYTES: help fight viruses and make antibodies.
Red blood cell is also known as ERYTHROCYTES, helps in oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
Platelets also known as THROMBOCYTES, helps in blood clotting.
- LEUKOCYTES: Leukocytosis: WBCs count higher than 11000 Causes: Autoimmune and inflammatory disease, Bacterial or viral infections, Cancers such as Leukemia, Allergic reaction, Stress etc. Leukopenia: WBCs count lower than 4000 Causes: Bone marrow failure, HIV/AIDS, Cancer, Vitamin deficiency etc.
FACTS REGARDING WBCs:
Also called SOLDIERS of the body. Made in the BONE MARROW. Lifespan = 13 – 20 days Have SHORT lifespan. Destroyed by the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM of the body.
RBCs
RBCS also called Erythrocytes 4.5 – 5.5 million. ANEMIA = Decrease RBCs POLYCYTHEMIA = Increase RBCs HEMOGLOBIN (Hgb) : HEMATOCRIT (Hct): MEN 14-18g/dl 42-52% WOMEN 12-16g/dl 37-47%
- RBCs indices: Mcv – (size of the RBC) 80-100fl ( femtoliters ) mcH – (amount Hgb in RBC) 27-33 pg ( picograms per cell ) mcHc- ( concentration of Hgb in RBC) 33-36 g/dl RBW- ( variation of RBC size ) 11-15%
PLATELETS 150,000 – 400,000
- THROMBOCYTOSIS = increase platelets count
Risk for clotting Inflammation disease Acute blood loss
- THROMBOCYTOPENIA = decrease platelets count
Risk for bleeding Bone marrow issues Viral infection Chemo
NORMAL RANGES WITH FULL FORM
mpv = mean platelets volume (7-10 fl ) ( average amount of the platelets ) .
WBC = white blood cell (5000-10,000)
RBC = red blood cell ( 4.5 5.5 million )
Hgb = hemoglobin (12.0 – 16.0 g/dl )
Hct = hematocrit ( 37-47 % )
MCV = mean corpuscular volume ( 81 – 101 fL )
MCH = mean corpuscular hemoglobin (26 – 34 pg )
MCHC = mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (32 – 36 g/L)
RDW = red blood cell distribution width ( 11.5 – 14.5 %)
PLT = platelets count ( 1,50,000 – 400,000)
MPV = mean platelet count ( 7 – 10 Fl )
Neut% = neutrophil percentage (40 – 70 %)
Abs Neut = absolute neutrophil (2500-6000) abs (a measure of the number of neutrophils in the blood)
Ly% = lymphocytes percentages (20 – 40 %)
Abs Ly = absolute lymphocyte (1000-4800 per microliter)
Mo% = monocytes (4-13 %)
Abs Mono = absolute monocytes (1 – 10 %)
Eos% = eosinophil percentage (0 – 5 %)
Abs Eos = absolute eosinophil (less than 500 cells per microliter)
Baso% = basophil percentage (0.1 – 2 %)
Abs Baso = absolute basophils (0 – 300 basophils per microliter of blood)
FACTS ABOUT RBCs AND PLATELETS
RBCs bring oxygen to the tissues in your body and release carbon dioxide to your lungs for you to exhale.
Develop in body’s bone marrow and release into bloodstream after they fully mature, which takes about 7 days
Bright red in color because of the presence of the protein (hemoglobin)
Do not have nucleus (allowing them to change shape and move throughout your body easier. )
Blood appear red because RBCs make up 40% of blood.
Lifespan = 120days
PLATELETS = react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot.
Usually survive for 7-10 days
Average healthy adult produces about 100 billion platelets.
Do not have nucleus.