Who is travel nurse?
Professional Definition: A travel nurse is a registered nurse (RN) who is employed on a temporary basis to work in different healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, or long-term care facilities. They are typically contracted through travel nursing agencies to fill staffing shortages or meet increased patient demands. These assignments can range from a few weeks to several months and often include benefits like housing stipends, travel reimbursements, and competitive pay.
Functional Definition: A travel nurse is a healthcare professional who temporarily relocates to various locations to provide medical care where there is a shortage of nursing staff. This role requires adaptability and versatility, as travel nurses must quickly acclimate to new environments, work with diverse patient populations, and handle various medical conditions and procedures. Their flexibility and willingness to travel make them crucial in maintaining healthcare services during staffing crises, seasonal fluctuations, or emergency situations.
Why travel nurses are in demand now-days?

Travel nurses are in high demand for several key reasons:
- Staffing Shortages: Many healthcare facilities face ongoing shortages of nursing staff due to retirements, burnout, and insufficient numbers of new nurses entering the workforce. Travel nurses help fill these gaps, ensuring patient care remains uninterrupted.
- Fluctuating Patient Volumes: Hospitals and clinics often experience seasonal or situational spikes in patient volumes, such as during flu season, pandemics, or natural disasters. Travel nurses provide the necessary support during these peak times.
- Specialized Skills: Travel nurses often possess specialized skills or certifications that are in short supply in certain areas. Their expertise allows healthcare facilities to meet specific medical needs without permanently hiring new staff.
- Cost Efficiency: Hiring travel nurses on a temporary basis can be more cost-effective for healthcare facilities compared to the long-term costs associated with full-time employees, such as benefits and pensions.
- Flexibility: Travel nurses offer a flexible workforce that can be rapidly deployed to areas of urgent need, providing a versatile solution to immediate staffing challenges.
- Geographical Imbalances: Some regions, especially rural or underserved urban areas, struggle to attract and retain permanent nursing staff. Travel nurses help bridge this gap by bringing skilled care to these locations.
- Regulatory and Policy Changes: Healthcare regulations and policies can sometimes change rapidly, creating sudden demands for additional nursing staff to comply with new standards or to implement new programs and services. Travel nurses help facilities adapt to these changes swiftly.
Q: What qualifications do you need to become a travel nurse?
To become a travel nurse, you must be a registered nurse (RN) with an active nursing license. Most agencies prefer candidates with at least one to two years of clinical experience in their specialty. Additional certifications, such as Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS), can enhance job prospects.
Q: How long are travel nurse assignments typically?
Travel nurse assignments usually last between 8 to 26 weeks, with 13 weeks being the most common duration. However, the length of assignments can vary based on the facility’s needs and the nurse’s preferences.
Q: Do travel nurses receive benefits?
Yes, travel nurses often receive a range of benefits, including housing stipends or accommodations, travel reimbursements, health insurance, retirement plans, and sometimes bonuses. Benefits packages vary by agency and assignment.
Q: Can travel nurses choose their assignments?
Travel nurses generally have the flexibility to choose their assignments based on location, duration, and specialty. They work with recruiters from travel nursing agencies to find positions that best match their preferences and career goals.
Q: How does licensing work for travel nurses moving between states?
Travel nurses must have a valid nursing license for the state where they will be working. Many states participate in the Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC), allowing nurses to practice in multiple member states with a single multi-state license. For non-compact states, nurses must obtain individual state licenses, often with the assistance of their travel nursing agency.
Q: What challenges do travel nurses face?
Travel nurses may face challenges such as adapting to new work environments quickly, being away from family and friends, finding temporary housing, and navigating different healthcare systems and practices. Flexibility and adaptability are key to overcoming these challenges.
Q:How do travel nurses impact patient care?
Travel nurses help maintain high standards of patient care by filling staffing gaps and bringing specialized skills to facilities in need. Their presence ensures that patient care is not compromised during times of increased demand or staff shortages.
Q: Are travel nurses paid more than regular nurses?
Travel nurses often earn higher pay rates compared to permanent staff nurses due to the temporary nature of their assignments and the demand for their flexibility. This higher pay can also include housing stipends, travel allowances, and completion bonuses.
Q: How do travel nurses find assignments?
Travel nurses typically find assignments through travel nursing agencies. These agencies match nurses with job openings based on their skills, experience, and preferences. Nurses can also search for assignments through job boards and online platforms specific to travel nursing.
Q: What are some popular specialties for travel nurses?
Popular specialties for travel nurses include critical care, emergency room (ER), labor and delivery, operating room (OR), telemetry, and medical-surgical nursing. Specialized skills in these areas are often in high demand.
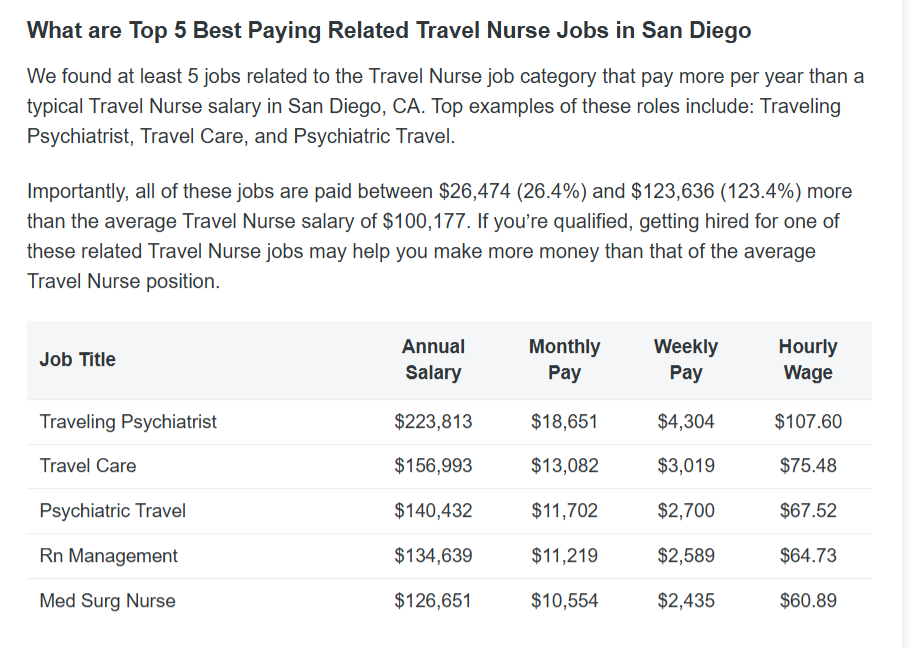
SALARY OF TRAVEL NURSES:
A travel nurse’s annual salary is a crucial aspect of their career. Travel nurses are known for their resilience in constantly changing work environments, ensuring timely and effective care for multiple patients. Their ability to cope with stress and remain focused enables them to thrive in diverse healthcare settings.
If you’re seeking new travel nurse job opportunities, visit [158 New Travel Nurse Job Postings on Indeed.com]
158 New Travel Nurse Job Postings | Indeed.com
Additionally, for international nurses aspiring to become registered nurses in Canada, refer to the comprehensive guide provided by Branded Nurses: [How to Become a Registered Nurse in Canada (Guide for International Nurses) Easy process 2024]
QUALITIES OF TRAVEL NURSE:
Travel nurses require a diverse set of qualities to excel in their roles. Here are few essential qualities along with examples of how they manifest in practice:
Adaptability:
Example: A travel nurse quickly acclimates to different hospital protocols and electronic medical record systems at each new assignment.
Flexibility:
Example: A travel nurse adjusts their schedule to accommodate last-minute shift changes or varying work hours, ensuring continuous patient care.
Strong Clinical Skills:
Example: A travel nurse with extensive ICU experience can manage critically ill patients effectively, providing high-quality care even in high-pressure situations.
Cultural Competence:
Example: A travel nurse working in a diverse urban hospital communicates effectively with patients from various cultural backgrounds, respecting their unique needs and preferences.
Problem-Solving Ability:
Example: When faced with a sudden equipment malfunction, a travel nurse quickly finds an alternative solution to continue administering treatment without delay.
Excellent Communication:
Example: A travel nurse collaborates seamlessly with a new team, clearly conveying patient information and care plans to ensure continuity of care.
Professionalism:
Example: A travel nurse maintains a positive and respectful attitude, adhering to the highest standards of nursing practice and ethics, even when facing challenging work environments.
Empathy and Compassion:
Example: A travel nurse provides emotional support to patients and their families, showing understanding and kindness during difficult health crises.
Time Management:
Example: A travel nurse efficiently prioritizes tasks and manages their workload to meet the needs of multiple patients, ensuring timely and effective care.
Resilience:
Example: A travel nurse copes well with the stress and demands of constantly changing work environments, remaining focused and dedicated to providing excellent patient care.
These qualities enable travel nurses to thrive in diverse healthcare settings, ensuring they deliver high-quality care regardless of the challenges they may face.

